Managing the Risk Involved in Healthcare Waste Management
Introduction The Healthcare sector produces significant waste, and 15% of this waste is hazardous material that could be infectious, toxic, or radioactive. Despite international and national agency frameworks and regulations to drive proper medical waste management, not all this waste is disposed of responsibly. Poor waste management in the healthcare sector poses several health risks, […]

Introduction
The Healthcare sector produces significant waste, and 15% of this waste is hazardous material that could be infectious, toxic, or radioactive. Despite international and national agency frameworks and regulations to drive proper medical waste management, not all this waste is disposed of responsibly. Poor waste management in the healthcare sector poses several health risks, including infections and water pollution, and can expose a healthcare company to legal or reputational risks.
Assessing a company’s waste management practices is crucial for investors to gauge adherence to global waste management regulations, which reduces potential legal and/or reputational risks. The ISS ESG Corporate Rating solution provides valuable insights for investors, enabling them to assess the effectiveness of waste management governance within healthcare organizations and make informed investment decisions with sustainability objectives.
The Problem
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), high-income countries produce, on average, up to 0.5 kg of hazardous waste per hospital bed daily, while low-income countries produce a daily average of 0.2 kg per bed (although the actual amount of hazardous healthcare waste in low-income countries might be higher). Further, a 2015 WHO/UNICEF assessment of sampled facilities from 24 countries found that slightly more than half had adequate systems for safe disposal of healthcare waste. This suggests that unsafe disposal of such waste is not rare.
Poor waste management in the healthcare sector can expose the general public to infections, drug-resistant microorganisms, and other harmful material being released into nature. Healthcare workers are particularly at risk from improper waste handling, which can lead to needlestick injuries and exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Medical waste, if not properly disposed of, can contaminate water bodies and the environment, leading to infectious diseases, air and water pollution, and loss of biodiversity.
Given these potential problems, health organizations are exposed to both financial and reputational risks if they fail to comply with regulations.
Regulations
Companies across the healthcare sector must consider regulations related to waste management. In the United States, for example, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) compliance requires establishing a waste management plan that encompasses both on-site and off-site management procedures, spanning from waste generation to final disposal.
In addition, industries within the health sector have considerations specific to them: for example, the pharmaceutical industry’s environmental impacts include chemical pollution during manufacturing and contamination from improper drug disposal. Addressing these impacts requires efforts to manage chemical use, improve wastewater treatment, and promote responsible drug disposal practices to minimize environmental harm.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set forth specific regulations in 2019 to ensure that pharmaceutical waste is responsibly managed. The EPA’s goals were to reduce pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater and to encourage recycling or reuse, as well as proper management of waste pharmaceuticals. Numerous healthcare facilities were impacted by these regulations, including retail pharmacies and pharmaceutical manufacturers operating as reverse distributors.
The EU Waste Directive (Directive 2008/98/EC) is not specific to hospitals. This directive applies to all waste streams, including healthcare waste, across Europe. It helps ensure that medical waste is treated and disposed of safely by categorizing various types of clinical waste under infectious waste. This ensures stringent handling, treatment, and disposal protocols are followed, thereby minimizing the risk of infection and environmental contamination throughout the region.
ESG Scoreboard: Analysis and Trends
Assessing a company’s waste management practices is crucial for investors to gauge adherence to waste management regulations. Compliance with strict regulatory laws, both domestically and internationally, underscores a commitment to legal adherence and environmental responsibility. Such a commitment reduces potential legal and/or reputational risks.
An integrated approach to managing healthcare waste involves acknowledging the diverse risks involved and implementing robust strategies and initiatives to mitigate them effectively. This includes considering the potential environmental and public health impacts of improper waste disposal, as well as the regulatory and reputational risks involved.
Leveraging ISS ESG Corporate Rating data, Figure 1 illustrates how companies in the Health Care Facilities & Services (HCFS) industry perform regarding waste reduction, treatment, and disposal. Company performance varies from poor (D+/D/D-) to excellent (A+/A/A-), with the former indicating little to no waste management practices and the latter comprehensive practices. Figure 1 shows that most HCFS companies score relatively low on this indicator.
Figure 1: HCFS Companies’ Performance on Waste Reduction, Treatment, and Disposal, February 2024
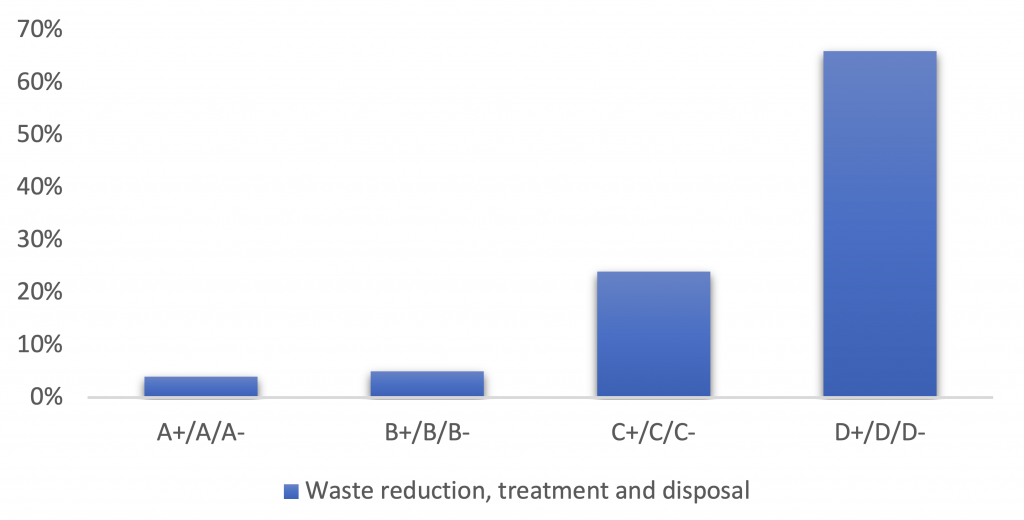
Source: ISS ESG
Companies that score high on waste management typically have practices that include advanced waste treatment methods such as incineration of chemical waste and autoclaving of infectious materials. Such practices highlight a commitment to thorough waste deactivation and sterilization.
According to research on metrics of companies in the ISS ESG Corporate Rating universe, the top-performing companies implement comprehensive measures aimed at reducing, treating, and disposing of waste. These measures encompass clear delineation of responsibilities, monitoring, targeted training programs, waste reduction objectives, promotion of bulk products with minimized packaging, adoption of reusable alternatives over disposable items, and systematic waste sorting and separation protocols. Companies that perform poorly on waste management tend to disclose high-level commitments to the waste management goal in their company policies but lack action plans with specific objectives.
Prioritizing effective waste management enhances companies’ long-term success by minimizing waste and resource consumption, boosting resilience and competitiveness, and adapting to evolving regulatory environments and consumer preferences, with waste management ratings serving as a key indicator of sustained performance. The ISS ESG Corporate Rating can help investors determine healthcare companies’ performance on waste management.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
By:
Ayushi Basu, Analyst, Corporate Ratings, ISS ESG
Neha Yadav, Analyst, Corporate Ratings, ISS ESG






















