Do Banks with a Greater Focus on Managing Value Chain Emissions Perform Better?
Many institutions have adopted measures to reduce their value chain emissions. These institutions include banks, which are increasingly committing to decarbonization strategies. ISS STOXX data provide insights into banks’ efforts to reduce value chain emissions and the relationship of these efforts to overall ESG performance and financial performance. Banks that perform well on decarbonization also […]

Many institutions have adopted measures to reduce their value chain emissions. These institutions include banks, which are increasingly committing to decarbonization strategies. ISS STOXX data provide insights into banks’ efforts to reduce value chain emissions and the relationship of these efforts to overall ESG performance and financial performance. Banks that perform well on decarbonization also tend to do well both on general ESG performance and financially.
Correlations among Decarbonization, ESG Performance, and Financial Performance
ISS STOXX evaluated over 300 banks globally. Each bank was evaluated on the Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain, which is calculated using the weighted score of three ISS ESG Corporate Rating underlying indicators:
- Carbon Footprint of the Corporate Value Chain, which assesses value chain emissions disclosure;
- Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy, which assesses bank strategies to address and/or reduce value chain emissions; and
- Monitoring & Reporting, which assesses the emissions avoided or mitigated through the bank’s efforts.
Each underlying indicator and the overall Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain is measured on a scale of 1.0 to 4.0, with a higher score indicating better performance.
A bank’s ESG performance score is determined by its aggregated performance in the topics of environmental, social, and governance indicators, as defined by the ISS ESG Corporate Rating Methodology, and is measured on a scale from 0 to 100.
The findings indicate that banks that perform better on Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain tend to have a high ESG performance score: a strong correlation (approximately 0.79) was present between these two factors (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain vs ESG Performance Score
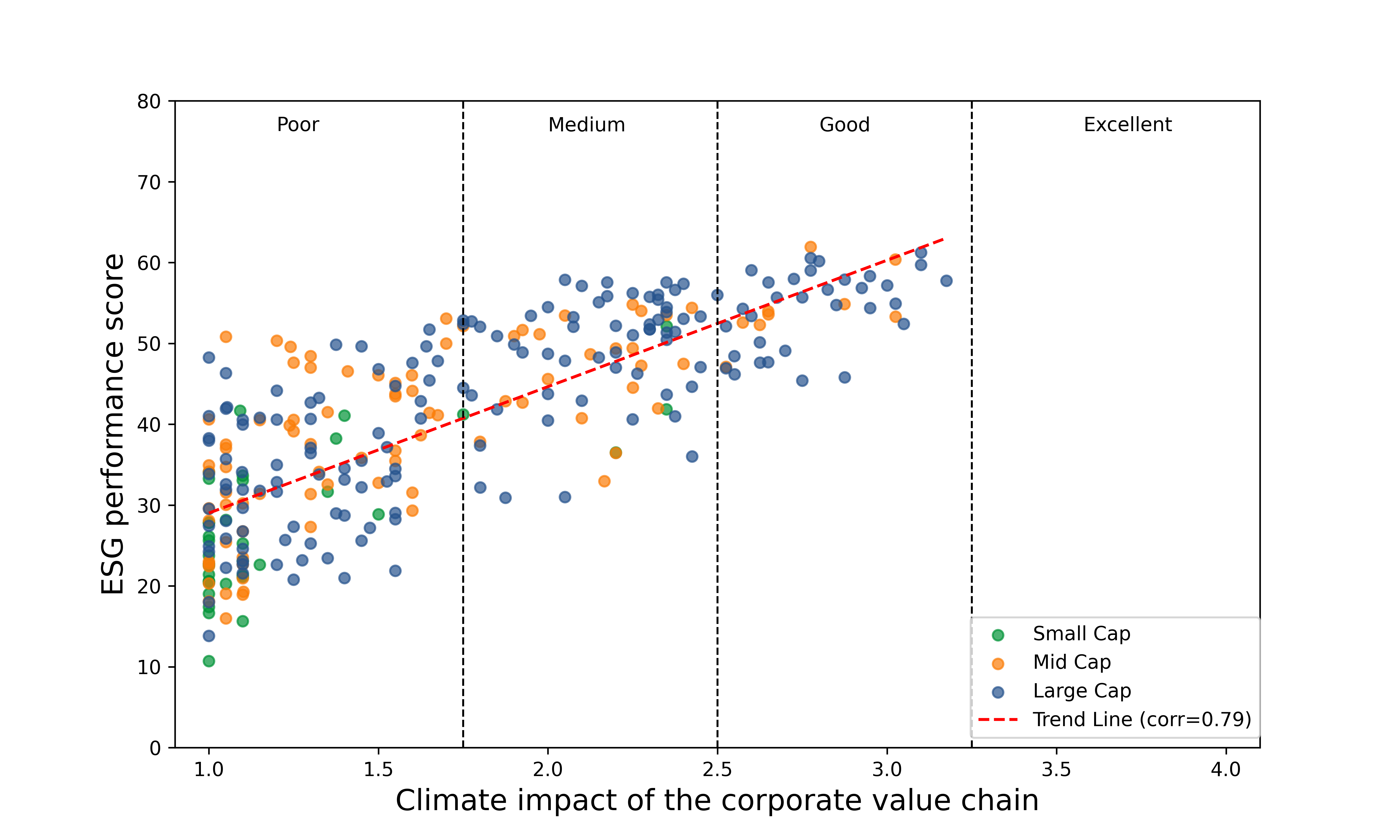
Source: ISS STOXX
The strong correlation between these two factors occurs both among banks from EU nations (excluding the United Kingdom) (correlation of 0.81) and banks from the United States (0.70).
Looking at the specific indicators within the Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain also displays correlations with ESG performance. For example, a high score on the Carbon Footprint of the Corporate Value Chain, reflecting a high degree of disclosure of value chain emissions, is directly correlated (0.68) to a high ESG performance score. This is expected, as banks that are transparent in reporting their value chain emissions tend to overperform in other segments of ESG.
A similar trend is observed in the transparency of the Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy (Figure 2). Banks with high or very high transparency scores have a high correlation (approximately 0.65) with their ESG performance scores. In contrast, the correlation remains low for banks with low or medium transparency scores.
Figure 2: Relationship among ESG Performance Score, Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy, and Transparency Level
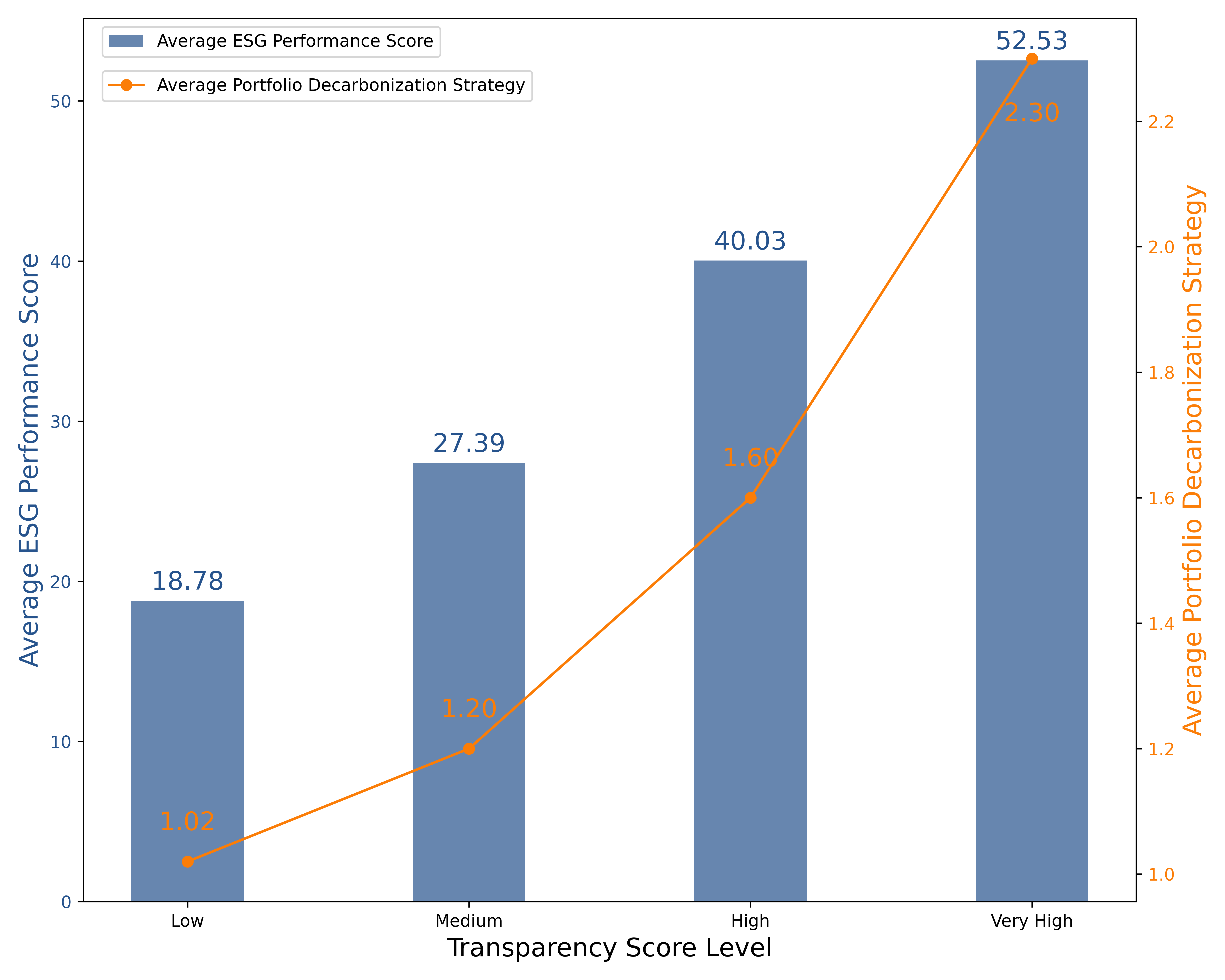
Note: Prime transparency score ≥ 50.
Source: ISS STOXX
This data varies with bank size. On average, large cap banks outperform mid and small cap banks both in their ESG scores as well as in their efforts related to corporate value chain emissions (Table 1).
Table 1: Banks’ Average ESG Performance Scores and Average Climate Impacts of the Corporate Value Chain, by Market Cap
Market Cap Average of ESG Performance Score Average Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain Large 43.13 1.86 Mid 39.92 1.62 Small 27.44 1.20
Note: The score of Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain topic is calculated using the weighted score of its underlying indicators, namely Carbon Footprint of the Corporate Value Chain (20%), Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy (60%), and Monitoring & Reporting (20%). The average topic score is calculated and displayed based on the market cap size of the banks.
Source: ISS STOXX
While none of the evaluated banks’ average scores for Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain crossed the ISS STOXX industry-specific Prime threshold of 2.00 (the equivalent of 50 for the ESG performance score), large cap banks performed better than others in this aspect. This is generally expected, as large cap banks are better equipped with resources for value chain disclosures, implementing decarbonization strategies, and providing green financing.
The average and standard deviation scores of the three indicators under this topic, such as the Carbon Footprint of the Portfolio, the Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy, and Monitoring & Reporting, follow a similar pattern as shown in Figure 3, which describes average performance of the banks for the above-mentioned indicators, based on their market capitalization.
Figure 3: Indicators of Banks’ Management of Portfolio Emissions, by Market Cap
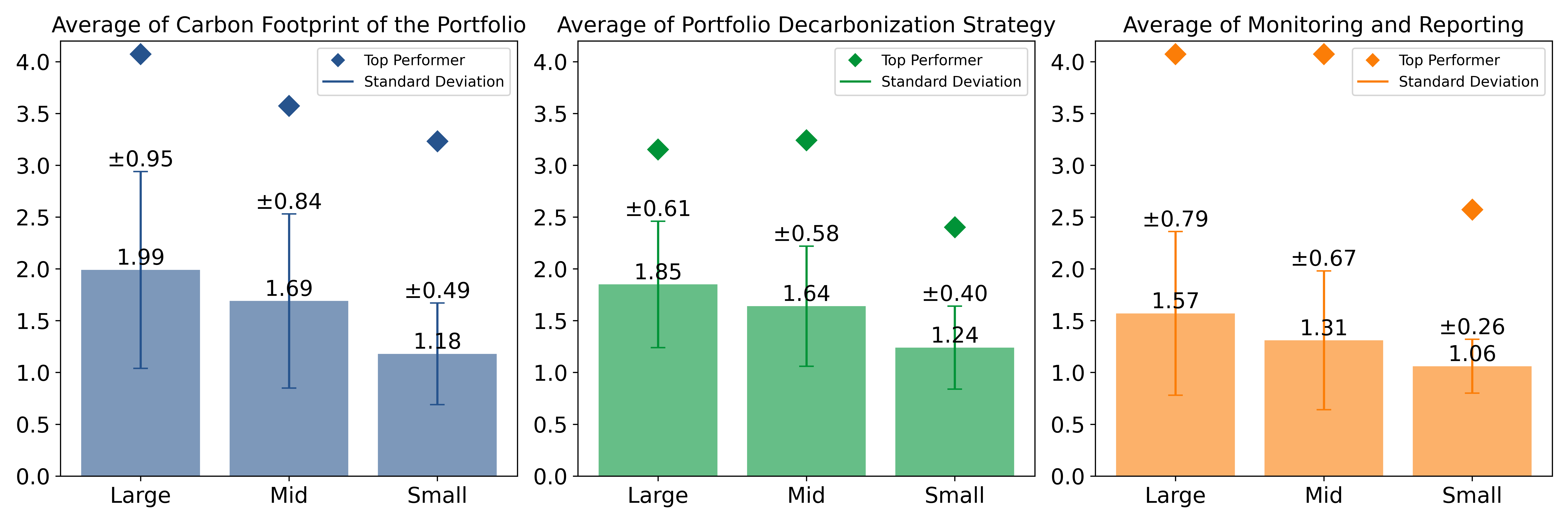
Source: ISS STOXX
The average indicator scores in each of the market cap categories exhibited outstanding performance; however, the average performance, even in the large cap category, remained below the industry-specific Prime threshold (2.00). Nevertheless, the standard deviation was substantially higher for large cap banks compared to small cap banks.
Management of portfolio emissions has financial implications as well. Table 2 compares banks’ average Portfolio Decarbonization Strategies with their average ISS Economic Value Added (EVA) Margins (EVA Margin is the profit margin that results after all operating expenses, taxes, and capital charges have been paid) and average financial profitability ratings (financial profitability is the percentile score of the stock’s profitability level based on its EVA as a percentage of sales and capital).
Table 2: Banks’ Average Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy, Financial Profitability Rating, and EVA Margin
Average Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy (1-4) Average Financial Profitability Rating (1-4) Average EVA Margin ≥2.00 2.84 7.50% <2.00 2.72 6.16%
Note: Of the three indicators under the Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain topic, Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy is the one presented here because it carries 60% of the weight of the Climate Impact of the Corporate Value Chain, making it the most important indicator.
Source: ISS STOXX
On average, banks with higher Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy scores outperformed those with lower scores by approximately 4.4% and 22%, suggesting a connection between banks’ financial performance and decarbonization efforts.
Conclusion
As shown by the data above, banks that outperform others in managing their portfolio emissions not only tend to be rated higher in the ISS STOXX ESG universe but also tend to have a superior financial profitability score, according to our proprietary EVA metrics.
Banks may be able to allocate towards decarbonization projects while maintaining a healthy balance sheet in the long run. Banks with higher exposure to companies with inferior decarbonization efforts could be exposed to undesired credit risk, since companies with poor decarbonization efforts may lag in complying with new regulations and market expectations. Such a lag may affect companies’ creditworthiness and leave banks financing these companies with impaired or non-performing loans. Investing in such laggard companies may also leave banks exposed to regulatory penalties, investor backlash, or reputation damage.
The ISS ESG Corporate Rating offers a holistic approach by providing ratings, data, and insights that can help investors identify banks that are leaders in decarbonization efforts and evaluate their preparedness for global regulatory updates in the field of climate change strategy. Granular information on an individual issuer’s decarbonization efforts and other industry-relevant data are also available to help investors and stakeholders make informed assessments.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
- Understand the F in ESGF using the ISS EVA solution.
By:
Gaurav Jagarwal, Senior Associate, Corporate Ratings Research, Financial & Real Estate, ISS STOXX
Roberto Lampl, Managing Director, Corporate Ratings Research, Global Multi Sector Head, ISS STOXX
Vanessa Liu, Analyst, Corporate Ratings Research, Financial & Real Estate, ISS STOXX






















